While Body Mass Index refers to your weight and height for a general health assessment, Waist-to-Hip Ratio tells you how your body’s fat distribution can predetermine health risks associated with excess abdominal fat.
Body Mass Index (BMI) and Waist-to-Hip Ratio (WHR) are simple ways to assess your health and risk of chronic diseases.
They offer different perspectives on your body composition and potential health risks!
How to Calculate Body Mass Index (BMI)
BMI is a widely used measurement that calculates your body fat based on your height and weight.
To get your BMI, divide your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared (kg/m²).
BMI = weight in kg / (height in meter)^2
The result is then categorized into different weight status categories:
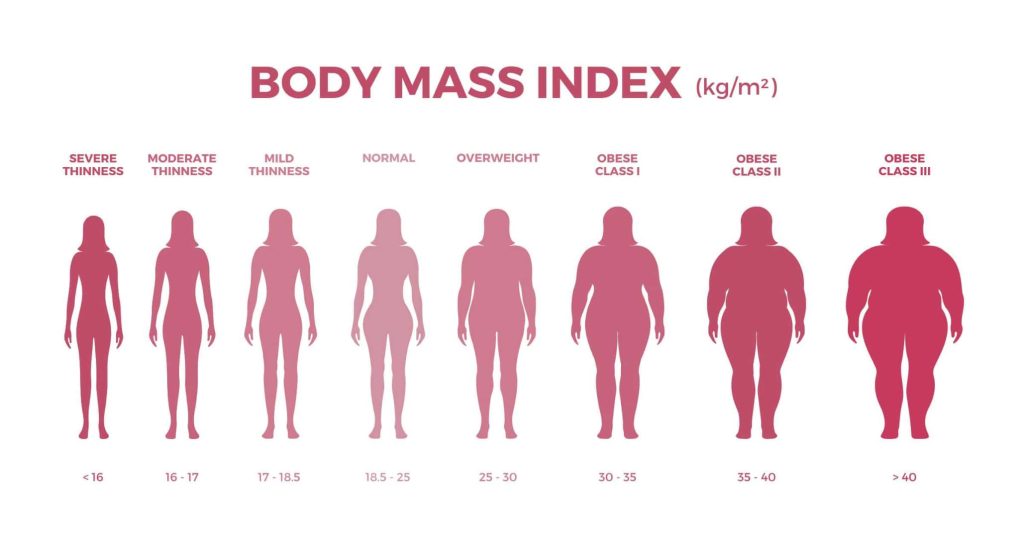
Limitations of BMI
While BMI is a convenient and easily accessible measurement, it also has limitations.
It does not distinguish between muscle mass and fat mass, which means muscular individuals may be categorized at a higher BMI despite being healthy and fit!
Additionally, BMI doesn’t account for the distribution of fat and muscle which offers different health insights.
How to Calculate Waist-to-Hip Ratio (WHR)
WHR compares the circumference of your waist to the circumference of your hips.
A higher WHR indicates a greater accumulation of fat around the abdomen.
Excess fat around the abdomen is associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases such as:
- cardiovascular disease
- type 2 diabetes
- metabolic syndrome
To calculate your waist-to-hip ratio, measure the circumference of your waist at the narrowest point and the circumference of your hips at the widest point. Then, divide your waist measurement by your hip measurement.

For example, if your waist measurement is 30 inches and your hip measurement is 40 inches, your waist-to-hip ratio would be 0.75.
The Importance of Both Measurements
While BMI and WHR provide different insights into your health, they are both valuable measurements for assessing your risk of chronic diseases and overall health status.
BMI is useful for:
- Assessing overall weight status
- Identifying individuals who may be at risk of obesity-related health problems.
However, it does not provide information about body fat distribution, which is an important determinant of health.
On the other hand, waist-to-hip ratio:
- Measures fat distribution around the abdomen, which is a significant predictor of health risks.
Research shows that individuals with a higher waist-to-hip ratio are more likely to develop obesity-related health conditions, regardless of their overall BMI. Therefore, incorporating both measurements into your health assessment can provide a more comprehensive picture of your health status.
How to Interpret the Results
Ideally, individuals should maintain their BMI within the normal weight range (18.5-24.9 kg/m²) and a waist-to-hip ratio below 0.85 for women and below 0.90 for men.
Staying within the range lowers the risk of chronic diseases and improves overall health outcomes. However, it’s important to remember that these measurements are just one piece of the puzzle and should be interpreted alongside other factors such as lifestyle, diet, and family history.
In a nutshell:
- Both BMI and WHR are valuable measurements for assessing your health status and risk of chronic diseases.
- Understanding and monitoring both measurements are important to take proactive steps toward maintaining a healthy weight and reducing your risk of obesity-related health problems.
- Focus on lifestyle changes such as healthy eating, regular exercise, and stress management to support overall health and well-being.
Talk to our trusted team of experts to know more about our holistic approach towards your body concerns. Book a consultation!